
Embryology Glossary Brain Vesicles Draw It to Know It
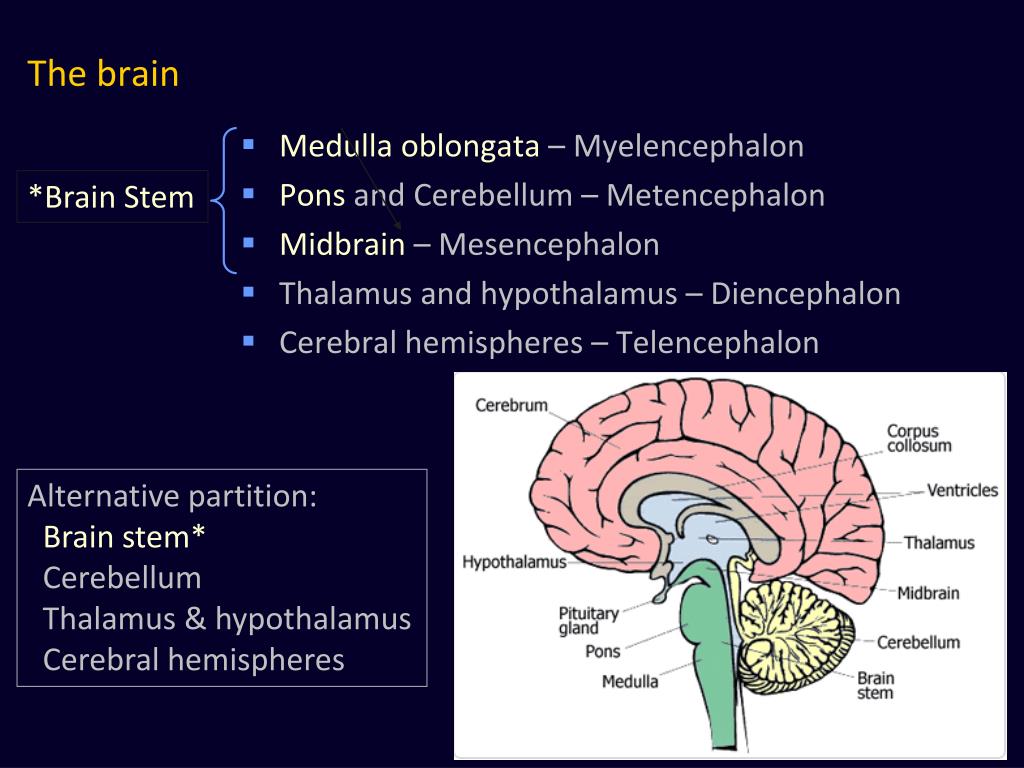
Myelencephalon. Metencephalon. The metencephalon has two major components: pons and cerebellum. Pons: The pons is part of the brainstem. It contains the rostral end of the fourth ventricle and gives rise to the trigeminal nerve. The pons has distinct ventral and dorsal parts. The ventral surface of the pons features bulging transverse pontine.
Neuroembryology Neupsy Key
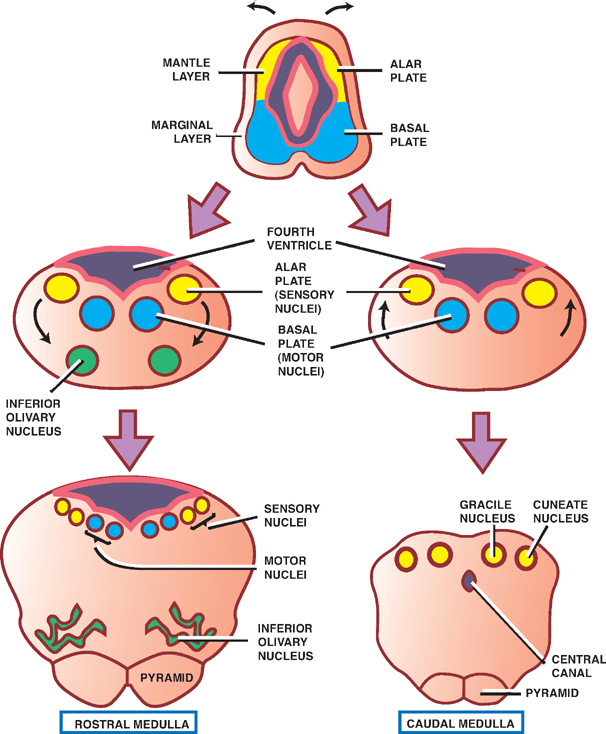
brain structure. In human nervous system: Medulla oblongata. The medulla oblongata (myelencephalon), the most caudal segment of the brainstem, appears as a conical expansion of the spinal cord. The roof plate of both the pons and the medulla is formed by the cerebellum and a membrane containing a cellular layer called the choroid plexus.

The Diencephalon Boundless Anatomy and Physiology
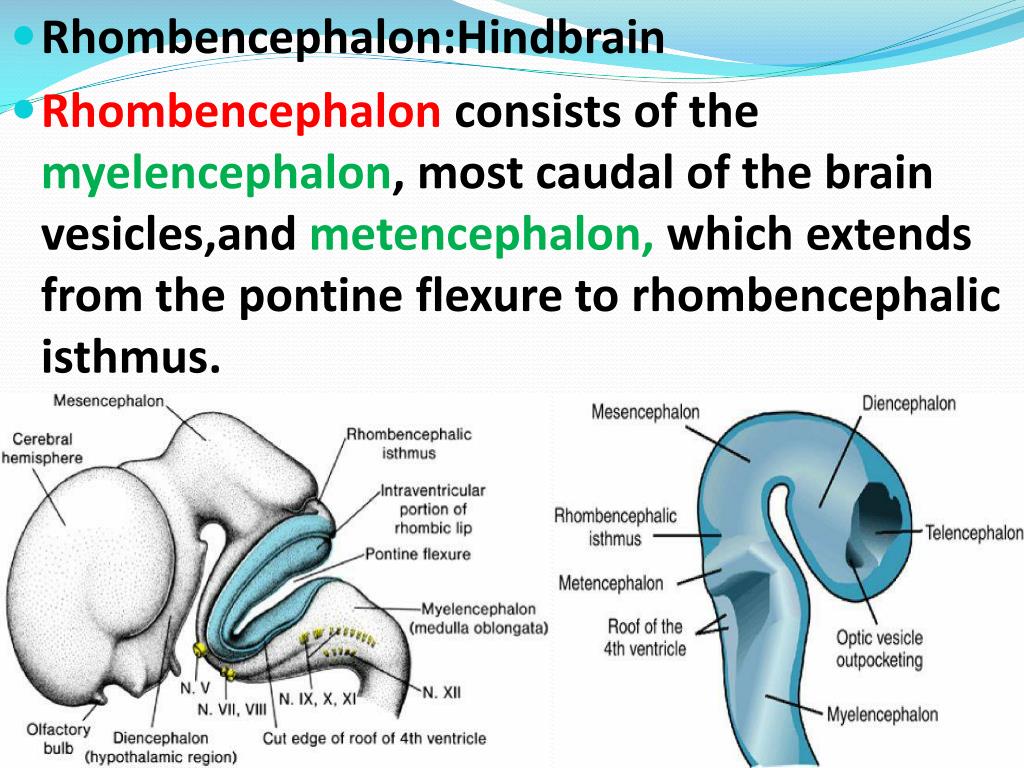
Anatomy of the encephalon: the hindbrain or rhombencephalon. The rhombencephalon or hindbrain is the lower portion of the brain. It surrounds the fourth cerebral ventricle and borders the lower part with the spinal cord. In fact, it's made up of the metencephalon, which contains the cerebellum and the bump, and the myelencephalon, which.
PPT Chapter 49 PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6108730
Medulla oblongata. Medulla oblongata is the terminal part of the brainstem.It sits in the posterior cranial fossa, below the tentorium cerebelli.The rostral medulla is continuous with the pons superiorly, with which it forms the pontomedullary junction. The caudal medulla continues onto the spinal cord inferiorly, just above the origin of the first pair of the cervical spinal nerves.

Anatomiediagramme
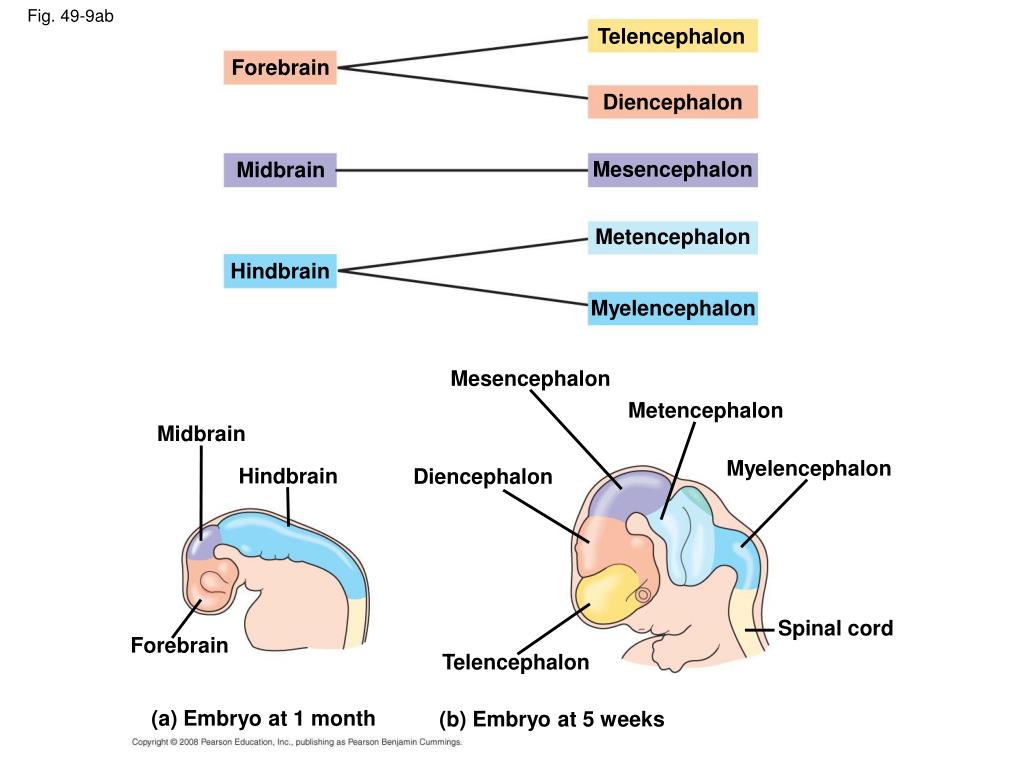
Myelencephalon. Diagram depicting the main subdivisions of the embryonic vertebrate brain. These regions will later differentiate into forebrain, midbrain and hindbrain structures. The myelencephalon or afterbrain[citation needed] is the most posterior region of the embryonic hindbrain, from which the medulla oblongata develops. [1]

6.1. Major Structures of the Myelencephalon Diagram Quizlet
The Ventricles, Choroid Plexus, and Cerebrospinal Fluid. J.J. Corbett, D.E. Haines, in Fundamental Neuroscience for Basic and Clinical Applications (Fifth Edition), 2018 Fourth Ventricle. The fourth ventricle is a roughly pyramid-shaped space that forms the cavity of the metencephalon and myelencephalon (Figs. 6.4 and 6.8).The apex of this ventricle extends into the base of the cerebellum, and.
PPT 3 Structure of the Nervous System PowerPoint Presentation ID3775987
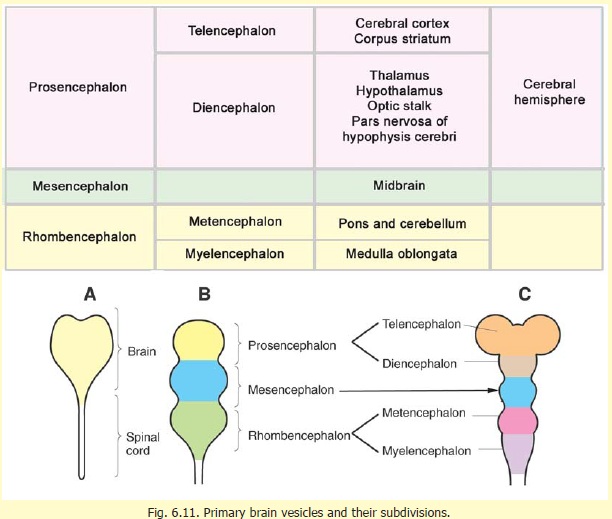
hindbrain, region of the developing vertebrate brain that is composed of the medulla oblongata, the pons, and the cerebellum.The hindbrain coordinates functions that are fundamental to survival, including respiratory rhythm, motor activity, sleep, and wakefulness.It is one of the three major developmental divisions of the brain; the other two are the midbrain and forebrain.

Physiology of CNS Sensory System By Dr Abdel
Human nervous system - Medulla, Brainstem, Reflexes: The medulla oblongata (myelencephalon), the most caudal segment of the brainstem, appears as a conical expansion of the spinal cord. The roof plate of both the pons and the medulla is formed by the cerebellum and a membrane containing a cellular layer called the choroid plexus, located in the fourth ventricle.

STOCK IMAGE, illustration of medulla development within the embryo at weeks five a eight b and
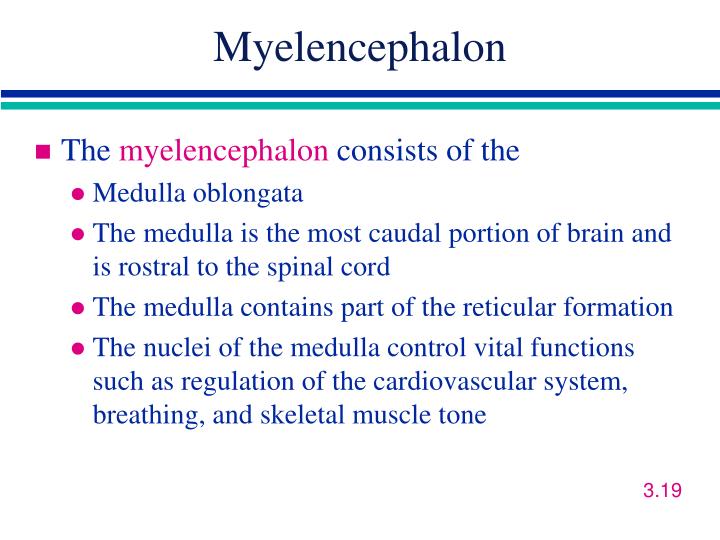
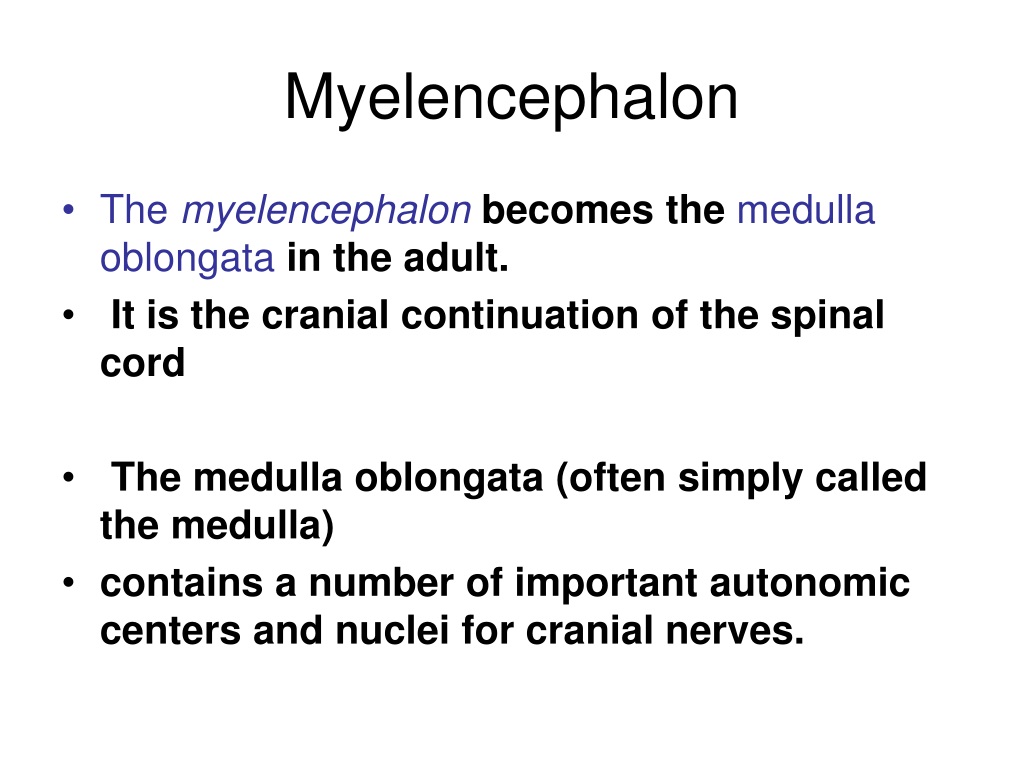
Myelencephalon. The myelencephalon consists of the medulla oblongata, which forms the brain posterior to the metencephalon and connects to the spinal cord ( Figures 7.76 and 7.77 ). The ventral fissure is the median ventral groove of the medulla. To either side are narrow longitudinal bands termed pyramids.
PPT II. Brain Structure PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4829280
The mesencephalon or midbrain is the portion of the brainstem that connects the hindbrain and the forebrain. A number of nerve tracts run through the midbrain that connect the cerebrum with the cerebellum and other hindbrain structures. A major function of the midbrain is to aid in movement as well as visual and auditory processing.

Myelencephalon Human anatomy, Organs, Map
Anatomical hierarchy. The myelencephalon or medulla oblongata (bulb is an archaic term) is the rostral continuation of spinal cord. It is the caudal part of the brainstem.It ends cranially at the medullopontine sulcus at the posterior border of the pons. Its caudal border lies along a plane above the root fibers of the first cervical segment.
PPT Development of the nervous system PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2633517
Figure 12.4.6 12.4. 6: Limbic System. The limbic system regulates emotion and other behaviors. It includes parts of the cerebral cortex located near the center of the brain, including the cingulate gyrus and the hippocampus as well as the thalamus, hypothalamus and amygdala. The amygdala is inferior to the hypothalamus.
PPT ANATOMY OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID9451375
Medulla oblongata (myelencephalon) adalah bagian bawah dari batang otak yang terhubung langsung ke sumsum tulang belakang. Ini merupakan bagian yang sangat penting untuk kelangsungan hidup. Fungsi bagian batang otak ini adalah mengatur aktivitas otonom, seperti pernapasan, detak jantung, dan tekanan darah.
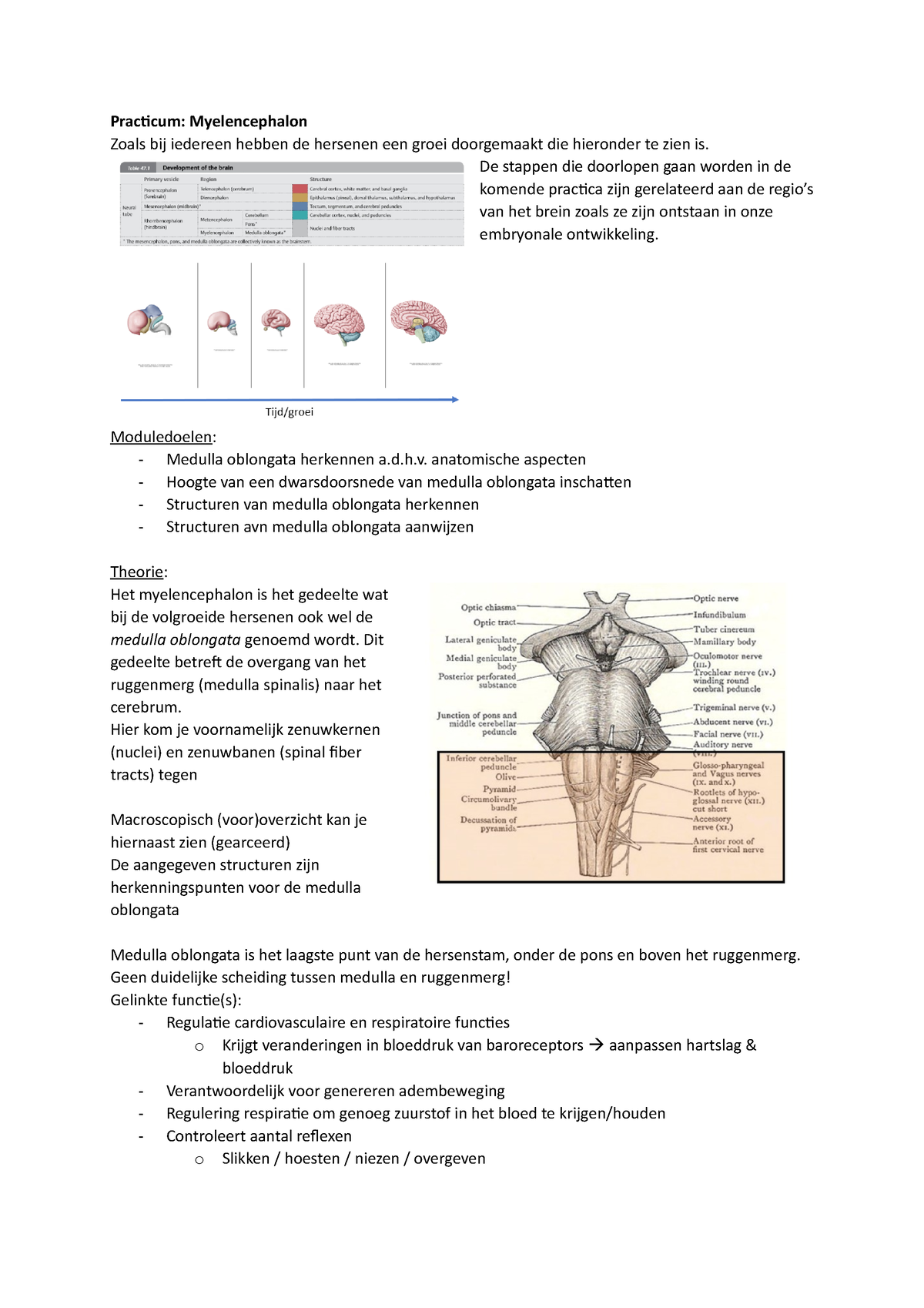
Myelencephalon Practicum Myelencephalon Zoals bij iedereen hebben de hersenen een groei
Otak adalah organ kompleks yang berperan sebagai pusat kendali tubuh. Sebagai komponen sistem saraf pusat , otak mengirim, menerima, memproses, dan mengarahkan informasi sensorik. Otak dibagi menjadi belahan kiri dan kanan oleh pita serat yang disebut corpus callosum . Ada tiga divisi utama otak, dengan masing-masing divisi melakukan fungsi.

Parts of the Brain The Hindbrain (Myelencephalon & Metencephalon) — . 3iCreative
The myelencephalon (medulla oblongata) gives rise to seven cranial nerves (VI through XII) and contains most of the fourth ventricle.A characteristic feature of the myelencephalon is the presence of bilateral pyramids along the ventral surface. The pyramids contain fibers which arise in the motor cortex and travel to the spinal cord as corticospinal fibers (the fibers run through the internal.
Subdivisions of Neural Tube
The myelencephalon represents the caudal part of the rhombencephalon.In adults it forms the medulla oblongata or bulbus spinalis. The myelencephalon accommodates most of the nucleus regions of the cranial nerves as well as the centers that monitor breathing, cardiac rhythm, swallowing, coughing, and vomiting, among others. It is a transition region between the spinal cord and the brain, so.