
PENGARUH PEMERIKSAAN OS PEDIS PROYEKSI ANTEROPOSTERIOR (AP) DENGAN ARAH SINAR TEGAK LURUS 0ᵒ DAN
Proyeksi: AP Axial Kaset: ukuran 24×30, grid kV: 70 mAs: 10 FFD= 100cm Posisi pasien: Supine di atas meja pemeriksaan Posisi objek: Atur MSP t ubuh pasien pada pertengahan kaset Kedua kaki dalam posisi lurus Tidak ada rotasi dari pelvis.
Gambaran radiograf terhadap posisi anatomi
Proyeksi AP bisa dilakukan pada pasien dengan posisi telentang, duduk, atau terlentang namun sudut batang badang 45 atau 90 derajat dari bidang datar. Prosedur ini biasanya dilakukan pada pasien yang tidak dapat berpindah tempat (mobilisasi) karena berbagai penyebab, sering kali terjadi pada pasien pasca bedah..

Gambar Proyeksi Isometrik dan Cara Membuatnya
Download scientific diagram | Gambar 3.11 Posisi pasien untuk proyeksi AP from publication: Teknik Radiografi Non Kontras 1 | Pemeriksaan radiografi merupakan teknik pemeriksaan pada organ tubuh.
Gudang Medis Teknik Radiografi Shoulder Joint
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data. The calcaneus axial view is part of the two view calcaneus series assessing the talocalcaneal joint and plantar aspects of the calcaneus. As technology advances, computed tomography (CT) has widely been used 1 to better visualize and characterize calcaneum fragment displacements and fracture lines.

Proyeksi vektor ortogonal vektor p=(4 5 3) pada vektor q...
This view is clinically indicated for trauma, chronic discomfort or infection of the elbow joint. It aids in visualizing fractures and/or dislocations of the elbow joint, in addition to osteomyelitis and arthritic changes. It is the preferred projection to assess the medial and lateral epicondyles of the humerus for avulsion-type fractures 2,3.
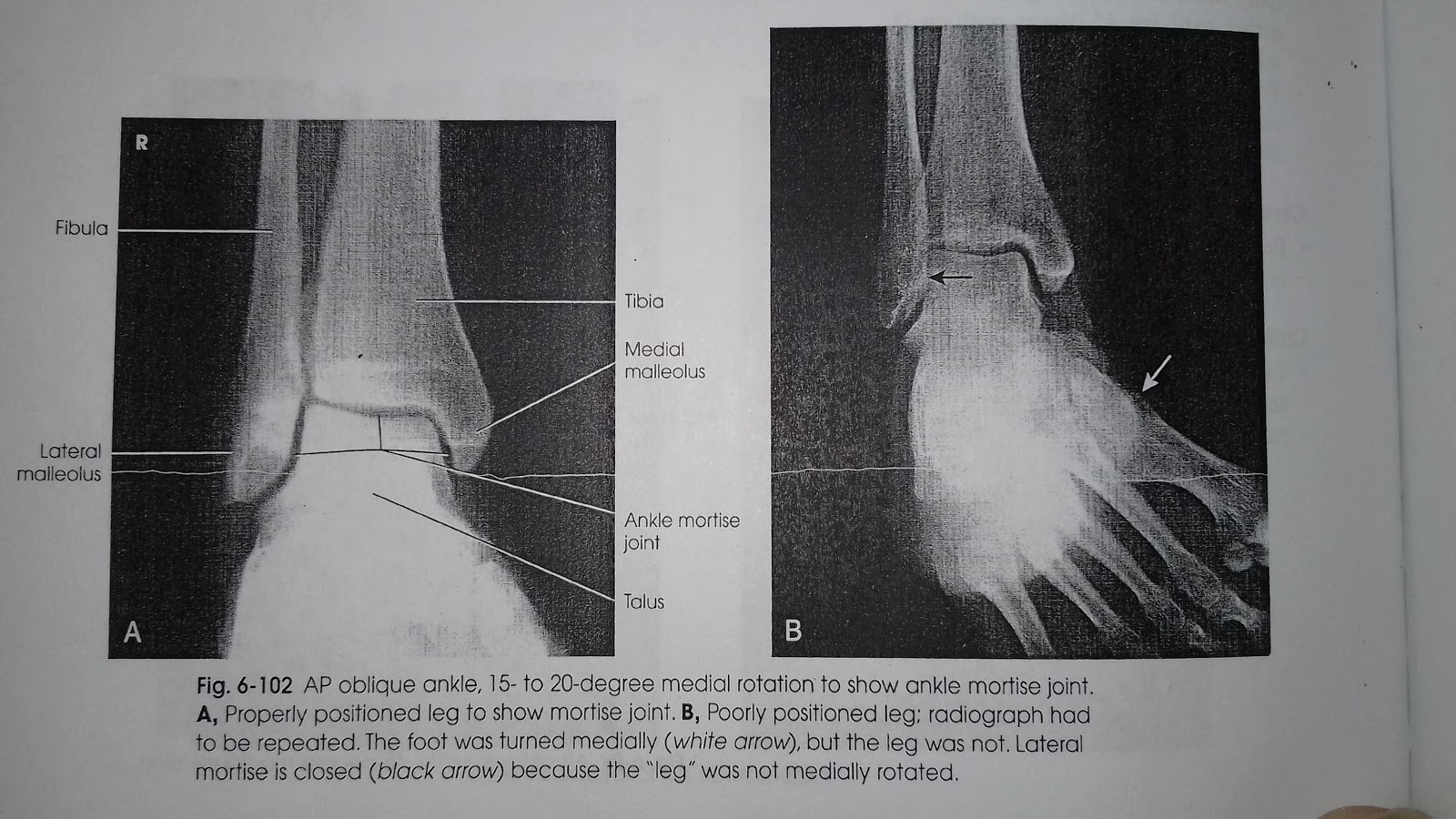
azizah nur Mortise joint proyeksi AP oblique (medial rotation)
Proyeksi AP axial outlet, CR 40 ° cephalad (bontrager,edisi 5) D. Proyeksi AP Axial "Inlet" Tujuan pemeriksaan : untuk menentukan daerah dislokasi pada trauma pelvis dibagian posterior dan untuk melihat adanya rotasi kedalam atau keluar dari pelvis anterior. Posisi Pasien : Pasien supine diatas meja pemeriksaan / brankard kepala diberi.

Proyeksi AP Supine dan Cross Table Lateral pada Pasien · PDF fileOPERASIONAL A. Kajian Teori
Proyeksi : AP. Kaset : ukuran 35 x 43 cm; kV : 60 ± 6 mAs : 6; FFD : 100 cm; Posisi Pasien : Pasien duduk menghadap meja pemeriksaan dengan tangan diletakkan di atas meja pemeriksaan, posisi telapak tangan menghadap ke atas. Posisi Obyek : Letakkan bahu pada meja pemeriksaan sehingga seluruh lengan terletak pada bidang horizontal yang sama
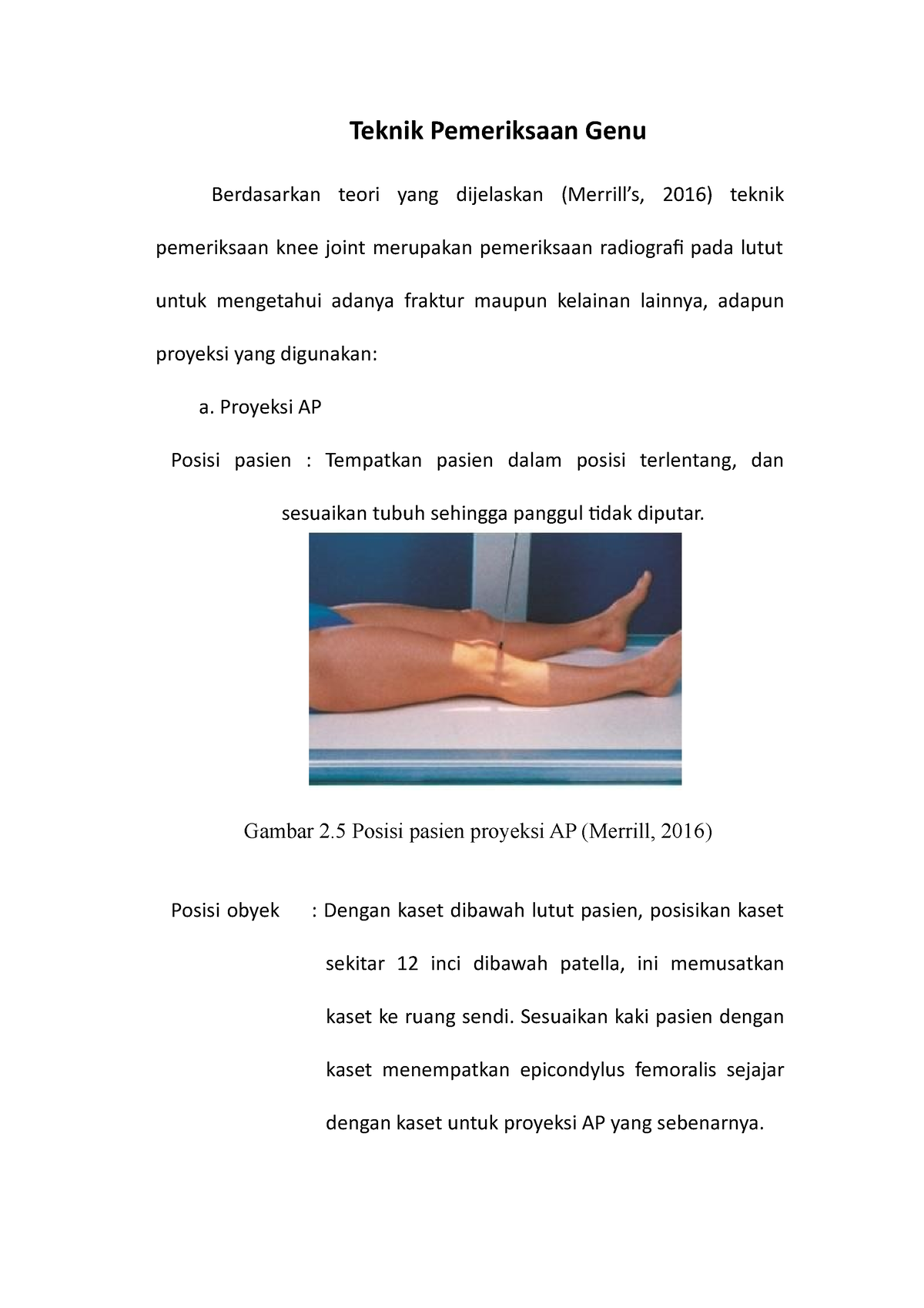
Teknik Pemeriksaan Genu Proyeksi AP Teknik Pemeriksaan Genu Berdasarkan teori yang dijelaskan
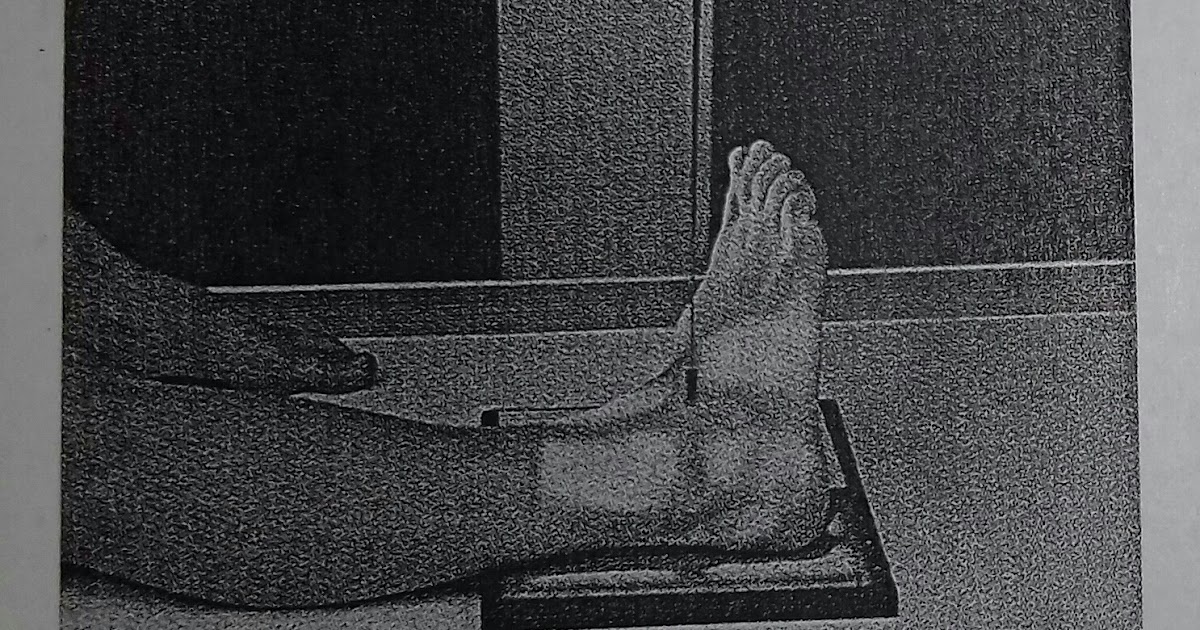
Proyeksi : AP . 1.Kaset : ukuran 24 x 30 cm. 2. kV : 60 ± 5 mAs : 2. 3. FFD : 100 cm. 4. Posisi Pasien : Pasien tidur di atas meja pemeriksaan, taruh bantal di kepala, lulut di tekuk flexi dan telapak kaki berada di atas kaset. 5. Posisi Obyek : Tempatkan telapak kaki lurus dan rata di atas permukaan kaset. Kaki sejajar dengan kaset dan CR

Prosedur pemeriksaan Radiografi Pedis Proyeksi AP Persiapan Pasien Untuk pemeriksaan pedis ini
Indications. Knee AP weight-bearing views will often be used in the context of orthopedic appointments to assess the alignment and degree of arthropathy when weight-bearing. This view is often used to assess osteoarthritis as non-weight bearing views can underestimate the degree of joint space loss. It is common for the AP view to include both.
azizah nur Mortise joint proyeksi AP oblique (medial rotation)
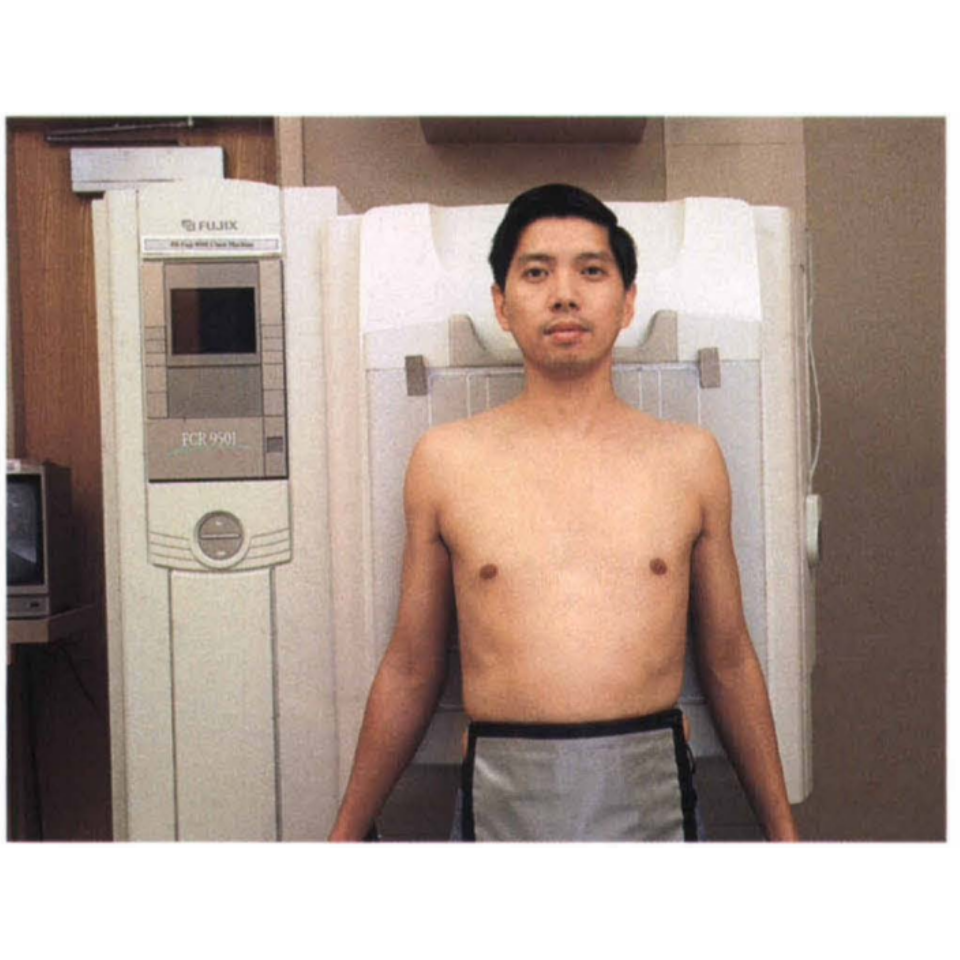
5. The chest radiograph assessement. 1. The difference between Chest Posterior Anterior (PA) and Anterior Posterior (AP) radiographs. Erect PA projections are considered the 'gold standard' for chest projection imaging (CXR). In some instances, it will not be possible to acquire an erect PA or even an erect AP image and the radiographer.

PA vs AP view... Medical radiography, Radiology student, Radiology technician
Proyeksi Abdomen Akut disebut juga dengan Proyeksi pemeriksaan Abdomen 3 posisi yaitu : AP. Setengah duduk. LLD. Proyeksi pemeriksaan AP. Persiapan pasien = Pasien dianjurkan untuk membuka baju hanya di sekitar perut saja. PP (Posisi pasien) = Pasien dalam posisi Supine atau tidur terlentang.

Teknik Pemeriksaan Radiografi Clavicula Proyeksi AP Dengan Indikasi1 PDF
AP view ; centering point. at the MSP, midway between the ASIS and the symphysis pubis 3; central ray . angled 15° cephalic 3; this angle allows the CR to be perpendicular to the sacrum as it is curved with an anterior concavity and convex posteriorly collimation. must adhere to the ALARA principle given the region exposed via the primary beam
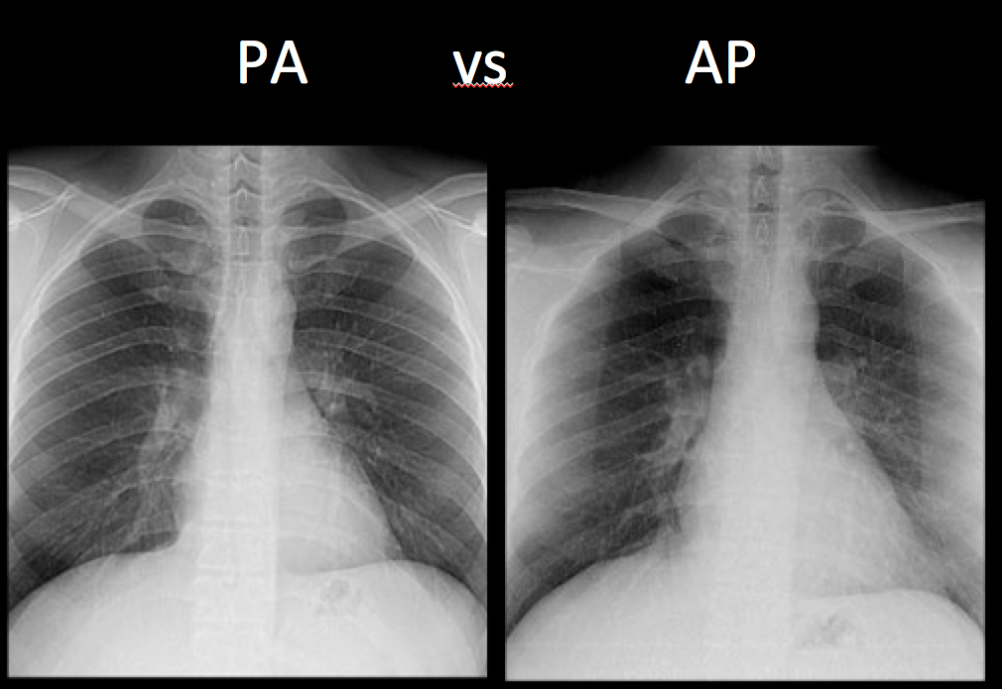
Chest XRay Basics PA vs. AP radRounds Radiology Network
Proyeksi : AP. Kaset : ukuran 24 x 30 cm; kV : 60 ± 6 mAs : 6; FFD : 100 cm; Posisi Pasien : Pasien duduk menghadap meja pemeriksaan dengan elbow extensi penuh; Posisi Obyek : Elbow ekstensi, tangan supine, dan sejajarkan lengan atas dan lengan bawah dengan kaset.

Teknik Pemeriksaan Radiografi Elbow Joint/ Cubiti Berbagi Itu Indah
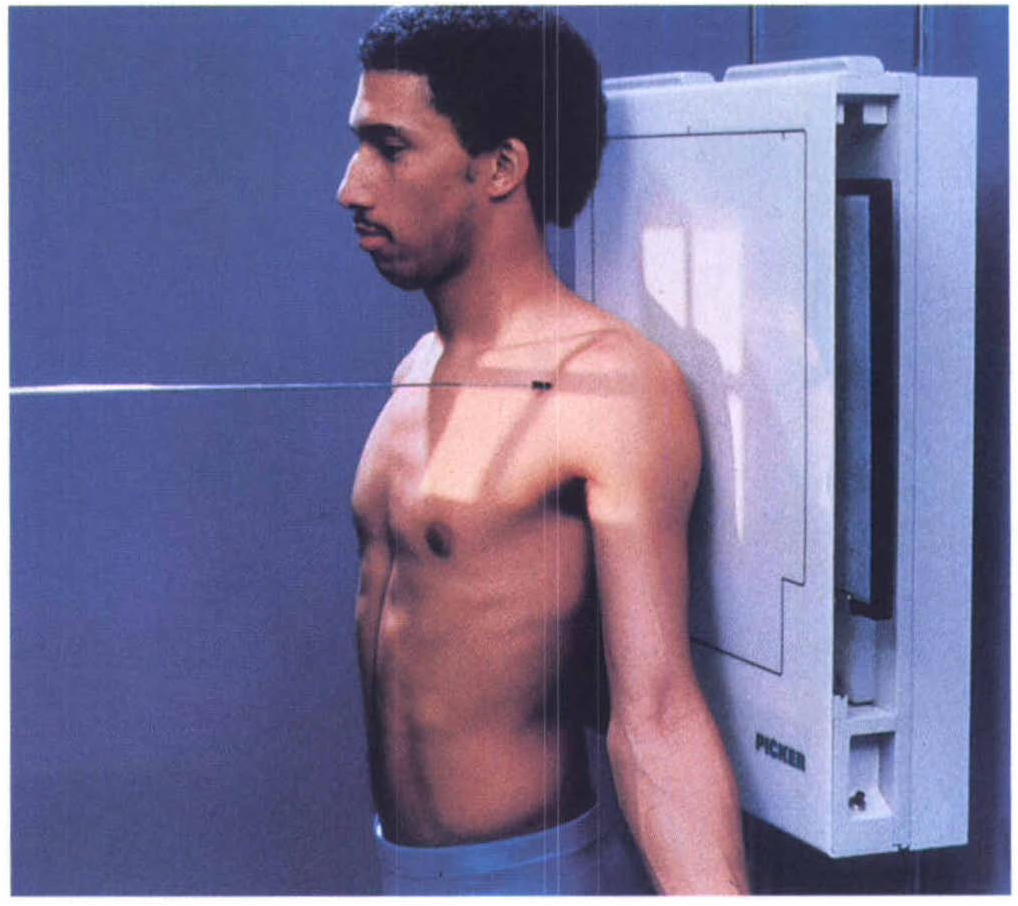
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data. The shoulder AP view is a standard projection that makes up the two view shoulder series. The projection demonstrates the shoulder in its natural anatomical position allowing for adequate radiographic examination of the entire clavicle and scapula, as well as the glenohumeral, acromioclavicular and.

azizah nur Mortise joint proyeksi AP oblique (medial rotation)
Teknik Pemeriksaan Radiografi Humerus. Proyeksi : AP. Posisi pasien erect atau supine. Pastikan shoulder dan elbow joints tidak terpotong. Putar tubuh ke lengan yang sakit sehingga lengan menempel ke kaset. Sejajarkan humerus dengan kaset, kecuali jika kaset harus di putar diagonal untuk memastikan shoulder dan elbow tidak terpotong.

Diketahui panjang proyeksi vektor a=(2 8 4) pada vektor
The AP view of the humerus is part of the humerus series and is usually taken in a standing position. However, it can also be obtained in a supine position. The projection demonstrates the humerus in its natural anatomical position allowing for adequate radiographic examination of the entire humerus and its respective articulations.