Chronic Hyperplastic Pulpitis Pulp Poly Oral Medicine YouTube
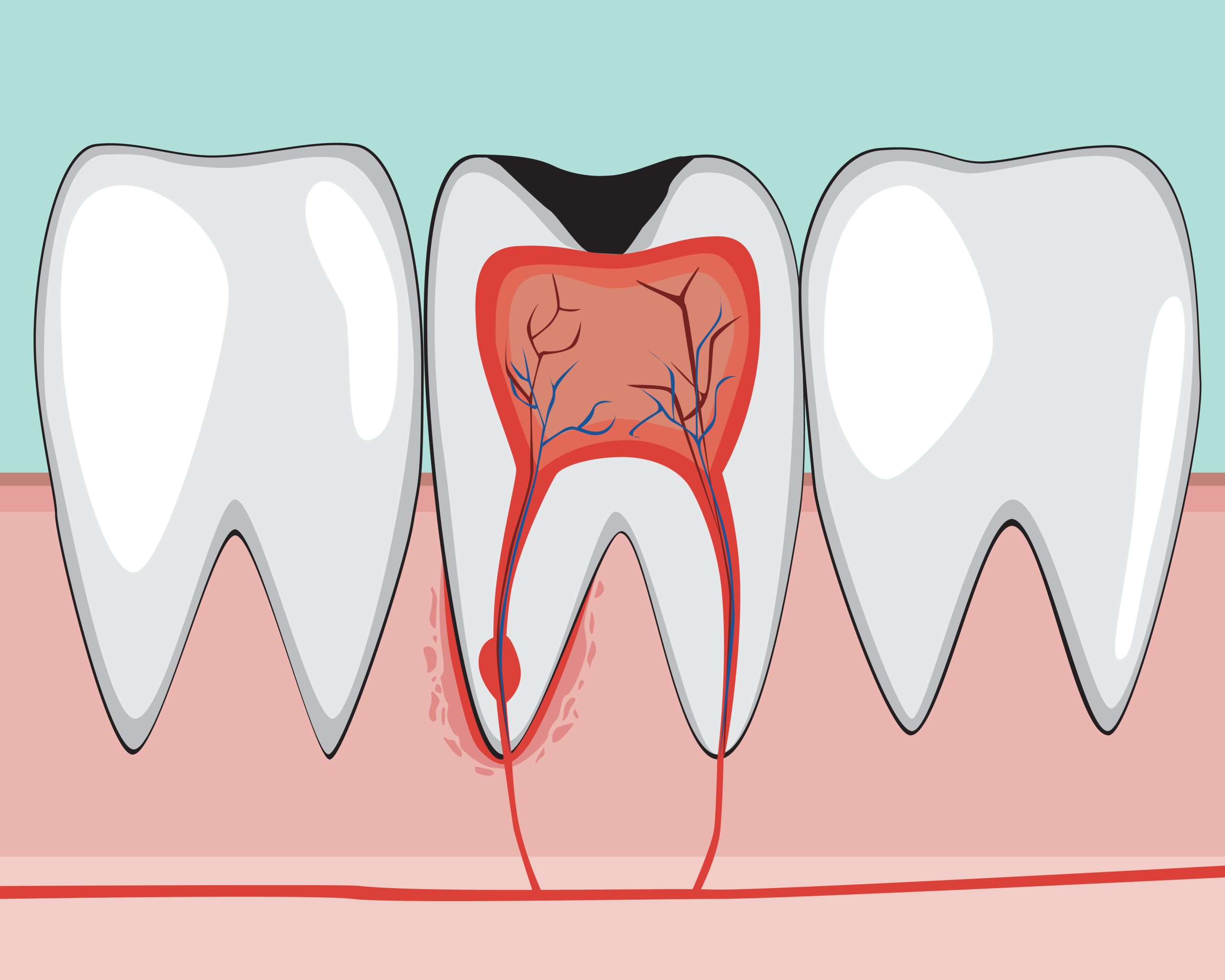
A pulp polyp, also known as chronic hyperplastic pulpitis, is a "productive" (i.e., growing) inflammation of dental pulp in which the development of granulation tissue is seen in response to persistent, low-grade mechanical irritation and bacterial invasion of the pulp.

Reversible Pulpitis Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment Endodontics YouTube
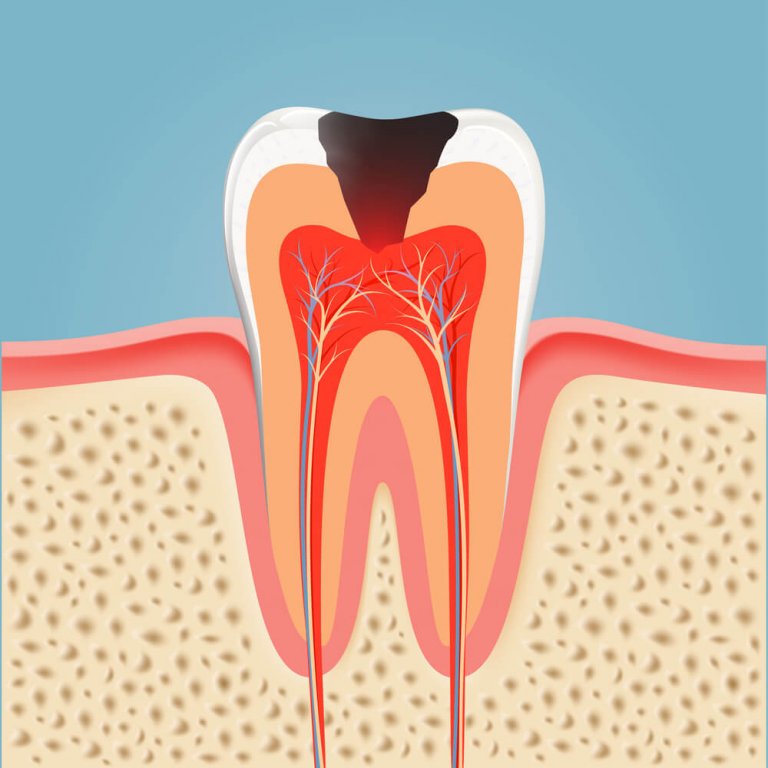
Hyperplastic pulpitis is a variety of chronic open pulpitis which is regarded as irreversible. This condition is usually treated by root canal treatment, unless coronal damage does not permit.

Pulp Polyp (Hyperplastic Pulpitis) What is it? Diagnosis, Treatment Endodontics YouTube
Chronic Hyperplastic pulpitis is one of the types of asymptomatic and irreversible pulpitis a patient may experience. It is an inflammation of the pulp due to extensive carious exposition in young or severely damaged teeth. The polyp may grow until covering the whole cavity. Sometimes the epithelium covers the space of the granulous tissue.
Pulpitis Reversible o Irreversible ≫Tratamientos Smysecret
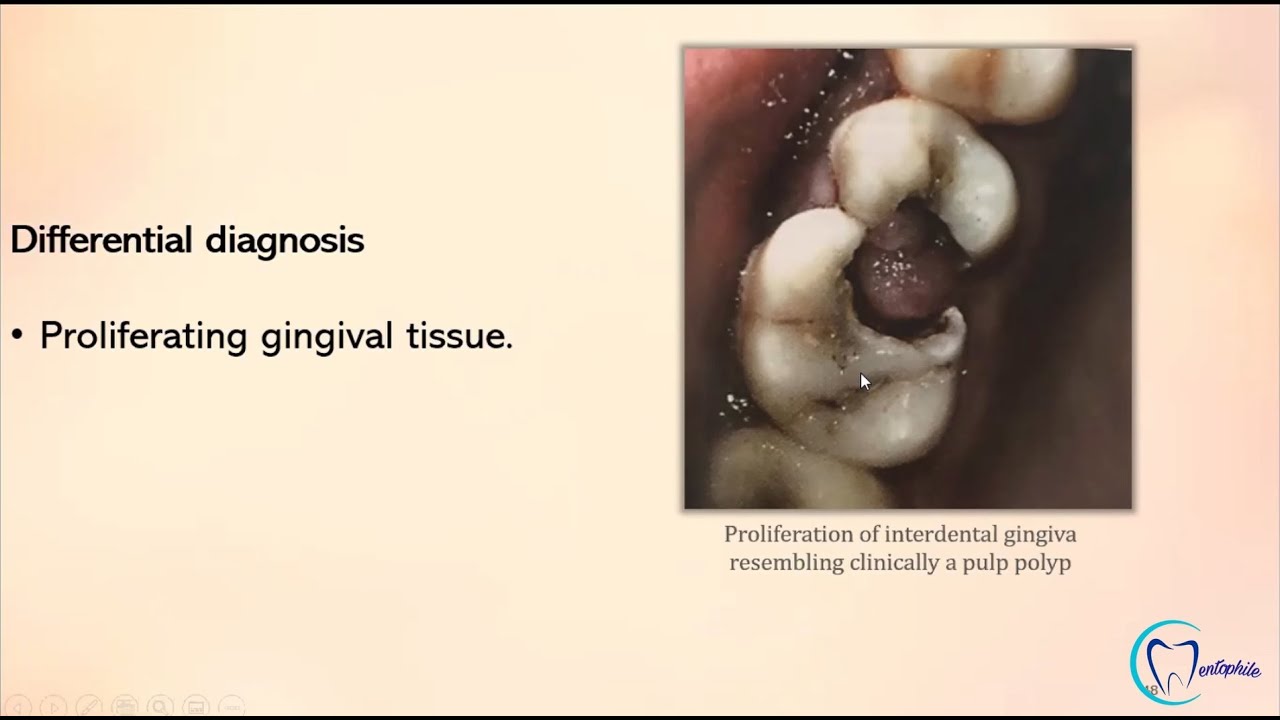
Chronic hyperplastic pulpitis (pulp polyps) usually occurs in molar teeth of children and young adults and is characterized by an overgrowth of granulomatous tissue into the carious cavity. Here, we report a rare type of pulp polyp in lower third molar of a 27-year-old woman that not only grow into carious cavity but also extruded in very large size that interfered with occluding of the teeth.

Symptomatic Irreversible Pulpitis Fully mechanical protocol (VDW.Rotate) tooth 15 YouTube
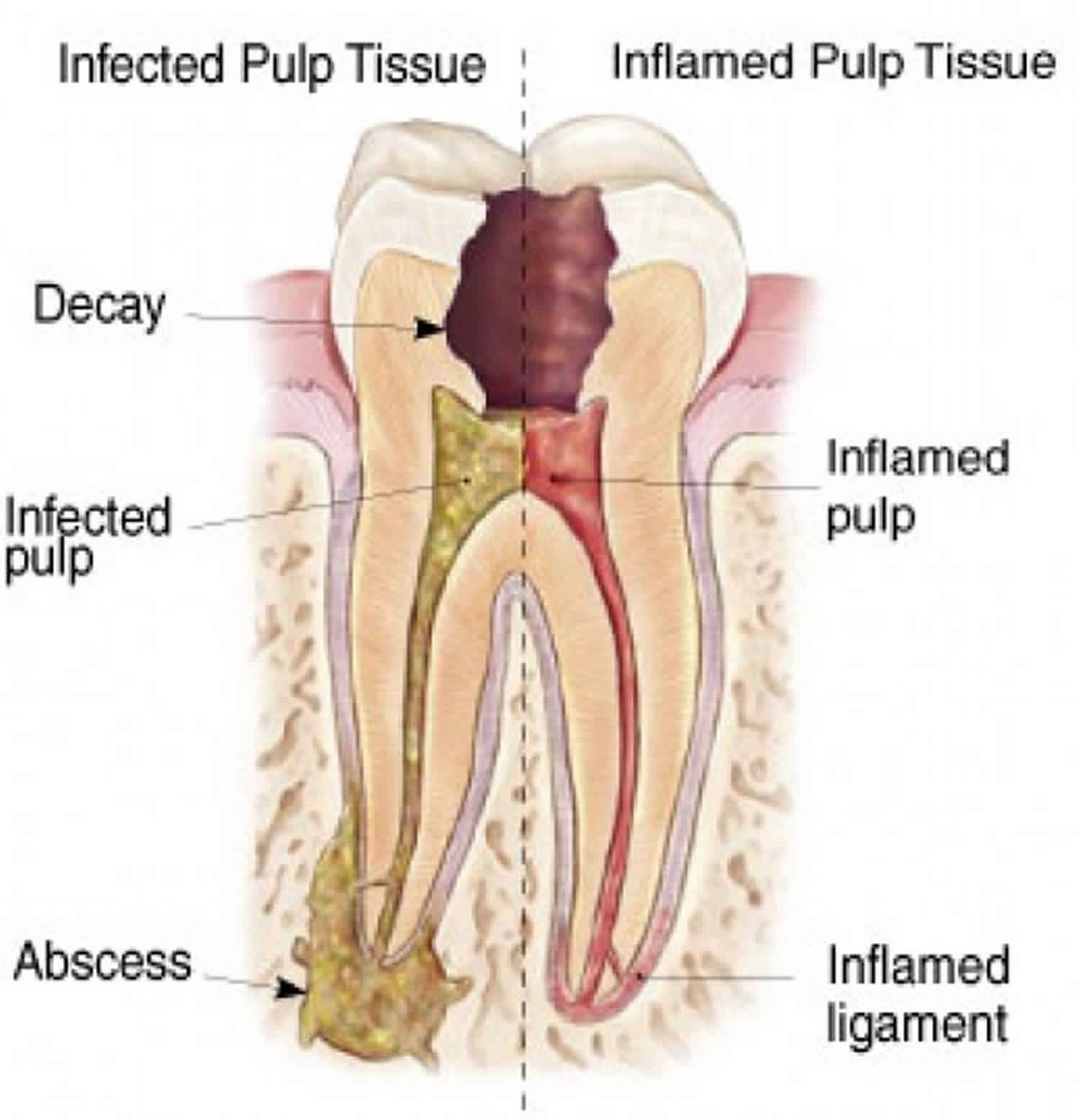
INTRODUCTION. Hyperplastic pulpitis is a type of irreversible chronic pulpitis that occurs usually in young teeth where the pulp has been exposed by caries or trauma ().Mechanical irritation and bacterial invasion result in a level of chronic inflammation that produces hyperplastic granulation tissue extrudes from the chamber and often fills the associated dentinal defect ().

Figure 1 from Partial Pulpotomy in a Permanent Molar with Hyperplastic Pulpitis A Case Report
Reversible pulpitis. K04.01 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2024 edition of ICD-10-CM K04.01 became effective on October 1, 2023. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of K04.01 - other international versions of ICD-10 K04.01 may differ.

Pulpitis Hiperplastik Kronis PDF
Pulpitis hiperplastik Pulpitis hiperplastik adalah bentuk dari pulpitis ireversibel dan sering dikenal dengan pulpa polip. Hal ini terjadi karena hasil dari proliferasi jaringan pulpa muda yang telah terinfalamasi akut.[13] Penyebab terjadinya pulpitis hiperplastik adalah vaskularisasi yang cukup pada

Hiperplastik Pulpitis Kronis.docx
10.1046/j.1365-2591.2003.00590.x. The purpose of this histological study was to examine teeth with hyperplastic pulpitis caused by trauma or caries. Key learning points: Hyperplastic pulpitis is a type of irreversible chronic open pulpitis. Young permanent teeth with hyperplastic pulpitis caused by trauma or caries have a great inherent.
What is Pulpitis? Symptoms, Treatment, and Pain Relief
Practice Essentials. The pulp polyp, also known as chronic hyperplastic pulpitis or proliferative pulpitis, is an uncommon and specific type of inflammatory hyperplasia that is associated with a nonvital tooth. See the image below. Pulp polyps involving the primary, first, and second mandibular molars in a young child with extensive dental caries.

PulpitisTypesCausesSymptomsTreatmentRisk FactorsPreventionDiagnosis
Chronic hyperplastic pulpitis (pulp polyps) usually occurs in molar teeth of children and young adults and is characterized by an overgrowth of granulomatous tissue into the carious cavity. Here, we report a rare type of pulp polyp in lower third molar of a 27-year-old woman that not only grow into carious cavity but also extruded in very large.

Pulpitis Gulf Coast Endodontics
Pulpitis hiperplastik tidak bisa sembuh dengan sendirinya. Jika dibiarkan begitu saja, penyakit gigi ini malah dapat memicu sejumlah komplikasi seperti yang telah disebutkan sebelumnya. Beberapa tindakan bisa Anda lakukan untuk mengatasi polip pulpa. Cara mengatasi pulpitis hiperplastik bisa dilakukan dengan tindakan medis atau mengonsumsi obat.

Benign Lesions of the Oral Cavity and the Jaws Pocket Dentistry
In the present study, 24 permanent teeth of individuals, aged 10-22 years and diagnosed as hyperplastic pulpitis were treated by pulpotomy using an atraumatic surgical technique with calcium hydroxide alone. The treatment was successful in 22 teeth, according to the following criteria: absence of clinical symptoms, absence of any intraradicular.
Pulpitis causes, symptoms, diagnosis & treatment
Chronic hyperplastic pulpitis (Pulp polyp) Content: Introduction Clinical features Histological features Treatment and Prognosis References Introduction: It is a unique form of chronic pulpitis that produces hyperplastic granulation tissue of pulp that extrudes from the pulp chamber like a polyp. Clinical features:

Diagnosis Pulpitis Alomedika
In the present study, 24 permanent teeth of individuals, aged 10-22 years and diagnosed as hyperplastic pulpitis were treated by pulpotomy using an atraumatic surgical technique with calcium hydroxide alone. The treatment was successful in 22 teeth, according to the following criteria: absence of clinical symptoms, absence of any.
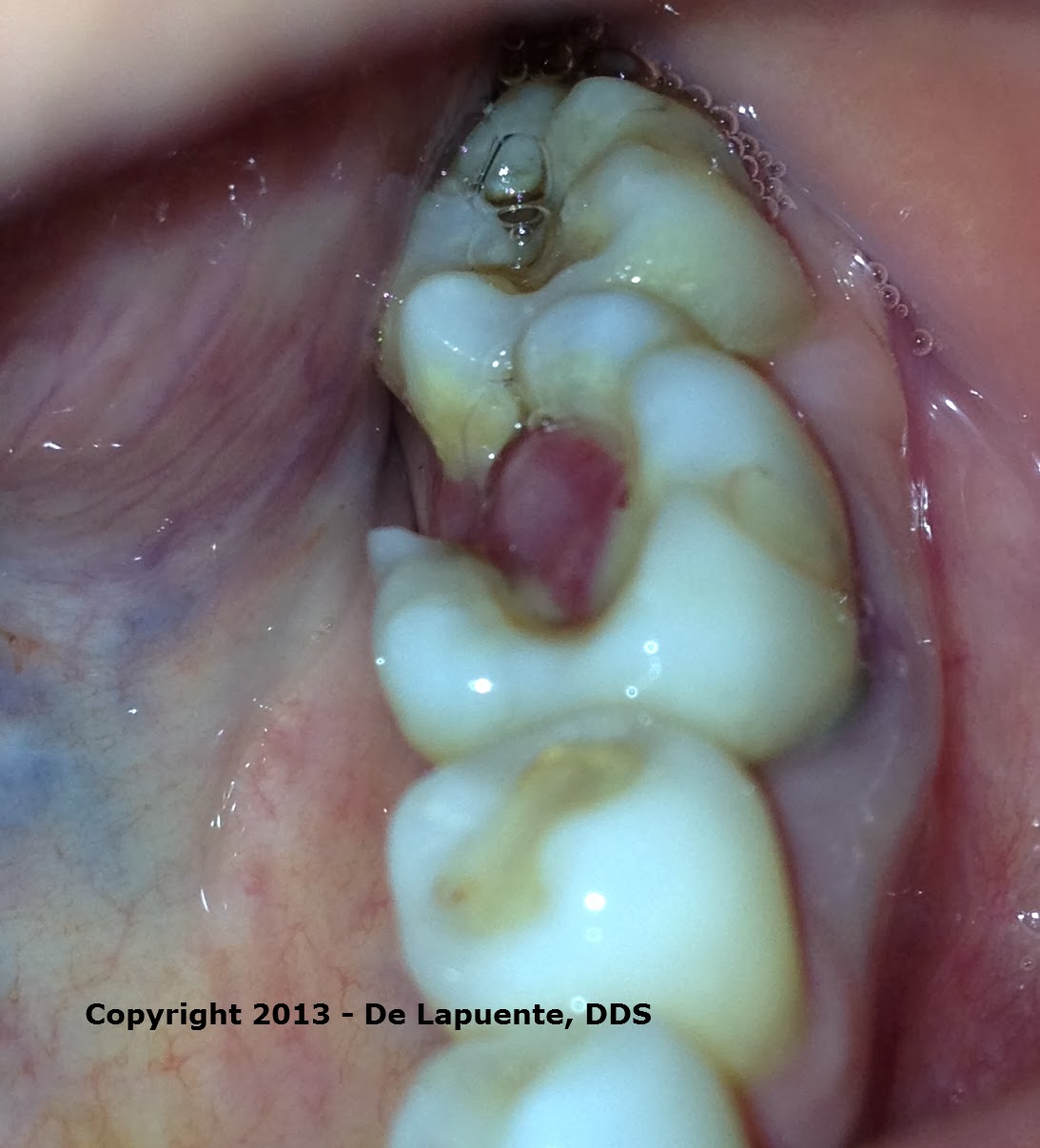
Diagnosing Oral & Maxillofacial Pathologies in My Residency CHRONIC HYPERPLASTIC PULPITIS (PULP
K04.01 Reversible pulpitis. K04.02 Irreversible pulpitis. K04.1 Necrosis of pulp. K04.2 Pulp degeneration. K04.3 Abnormal hard tissue formation in pulp. K04.4 Acute apical periodontitis of pulpal origin. K04.5 Chronic apical periodontitis. K04.6 Periapical abscess with sinus. K04.7 Periapical abscess without sinus.

PULPITIS HIPERPLASTIK KRONIS
Based on clinical and radiographic techniques, the presumptive diagnosis was hyperplastic irreversible pulpitis or PP. Signed informed consent (IC) was obtained from the legal guardian. The tissues were anaesthetised using locoregional techniques: nerve block of the inferior dental nerve with vestibular and intrapulpal reinforcement with 3%.